Carbohydrates (the more technical term for carbs) are a macromolecule. Carbohydrates are used as an immediate energy source in living things but they also give structure to a variety of organisms. Most carbohydrates have the ratio of 1:2:1 for carbon to hydrogen to oxygen.
Glucose is an example of a carbohydrate, but not just any carbohydrate, a monosaccharide to be specific. A monosaccharide is a simple sugar that canot be broken down by hydrolysis. Monosaccharides have this crazy name because "monos" means single and "sacchar" means sugar. Get it? It's made of only one single sugar; they are a simple sugar. Yeah, well now that you hopefully got that down I can tell you that these simple sugars can have a backbone of three to seven carbons. The molecular formula is some multiple of CH2O. Which means...that with every carbon item it is bonded to a H and a -OH molecule. However, this is not always true, there are a few exceptions. This is just the basic formula. Glucose has six carbon atoms and therefor called a hexose. its molecular formula is C6H12O6. Ribose, on the other hand, is made up of five carbon atoms and therefore called a pentos. But usually these monosaccharaides dont stay that way for long.
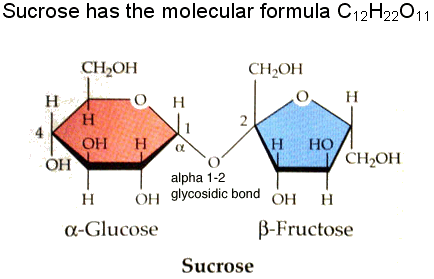
When two monosaccharides combine in a dehydration reaction you get a disaccharide. For example when you combine glucose and fructose (two monosaccharides) you get the disaccharide of sucrose, also known as table sugar. Sucrose is the form of sugar that is transported in plants. Another disaccharide, lactose, is made when glucose and galactose are combined. I'm sure you have heard of a few people who are lactose intolerant. This means that that person cannot break down the lactose disaccharide.
Polysaccharides are the next step up. Polysaccharides are polymers(macromolecule consisting of covalently bonded monomers) of monosaccharides or a bunch of monosaccharides combined together. These carbs can also be called complex carbohydrates. Some types of polysaccharides are used as short-term energy storage. These can be used as storage because they are not soluble and they are bigger than sugar. because of their large size they can't pass through the plasma membrane. When you need energy the pollysaccharide is broken down to release its sugar molecules.
 |
| These are polysaccharides that are found in plant cells |